Understanding Object-Oriented Programming: Unveiling the Power of Classes

Embarking on the journey into the world of Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) is similar to exploring...
Embarking on the journey into the world of Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) is similar to exploring a landscape filled with architectural blueprints. At the very heart of this programming paradigm resides a fundamental building block: 'Classes.' Much more than typical templates, classes serve as the backbone of OOP, enabling the creation of structured, modular, and reusable code. Understanding classes opens the doors to developing powerful software applications, organizing data, and defining behaviors. So, let's go into the heart of OOP and discover the significant impact of classes on creating elegant and effective solutions to real-world programming challenges.
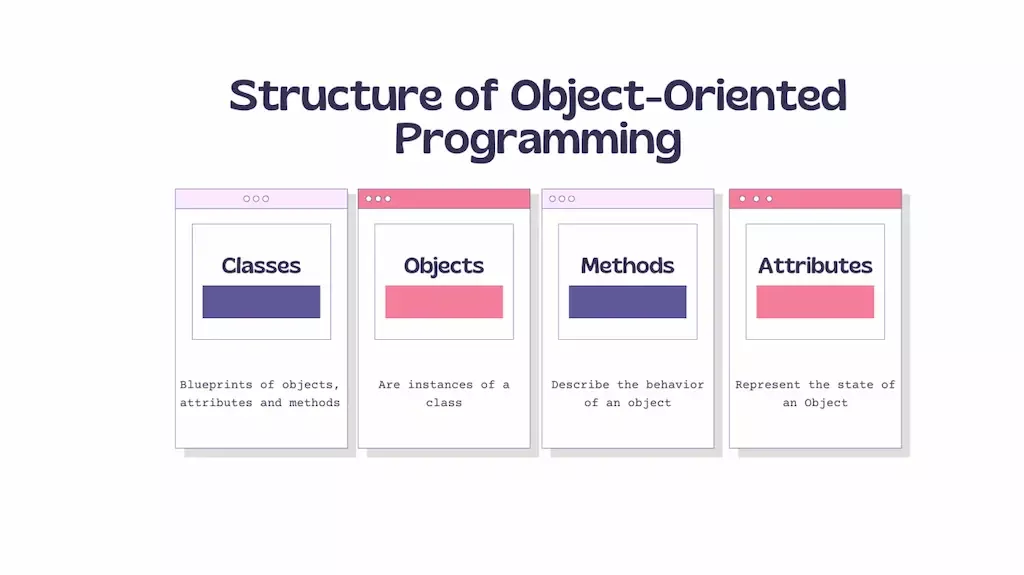
Classes
In the context ofObject-Oriented Programming (OOP), a class serves as a blueprint or template that defines the properties (attributes) and behaviors (methods) that objects belonging to that class will contain. It serves as a fundamental principle for organizing code and generating objects.
-
Blueprint or Template:A class defines the structure, attributes (properties), and behaviors (methods) that objects instantiated from that class will contain.
-
Properties (Attributes):These are the features or data associated with objects in the class. They represent the state of the object and are defined as fields within the class.
-
Behaviors (Methods):These are the actions or operations that objects in the class can perform. Methods explain what an object can do and how it can interact with other objects or the environment.
-
Fundamental Principle for Organizing Code:Classes provide an approach to organize code by grouping related data and functionalities into a single component. They promote modularity, re-usability, and maintainability in software development.
-
Generating Objects:Instances or objects are generated based on the blueprint provided by a class. Each object created from a class has its own set of properties and behaviors defined by that class.
//Class Example
public class Car
{
// Field
private string model;
// Property
public string Model
{
get { return model; }
set { model = value; }
}
// Constructor
public Car()
{
// Constructor logic
}
// Method
public void StartEngine()
{
// Method body
}
}

