
Scheduled backup of Vault secrets with Jenkins on Kubernetes

Experience related to automation of Vault backup creation using Jenkins scheduled job and simple python script which I built to create dump of vault secrets.
Experience related to automation of Vault backup creation using Jenkins scheduled job and simple python script which I built to create dump of vault secrets.
Let's start.
What is HashiCorp's Vault?
Vault is a tool for securely accessing secrets. A secret is anything that you want to tightly control access to, such as API keys, passwords, certificates, and more. Vault provides a unified interface to any secret while providing tight access control and recording a detailed audit log.
Prerequisites:
- Vault Installed
- Jenkins Installed
My Setup
- EKS Kubernetes cluster
- Vault runs on EKS cluster
- Jenkins runs on EKS cluster
You can read in this tutorial how to run Jenkins on EKS cluster:
https://igorzhivilo.com/jenkins/ci-cd-future-k8s-jenkins
What you will learn from this post?
-
How to use python hvac library for authentication with Vault programmatically and backup vault secrets.
-
What is AppRole authentication mechanism in Vault and how to enable/create it.
-
How to create scheduled backup for Vault secrets with Jenkins pipeline on k8s.
AppRole authentication method in Vault
How can an application programmatically request a token so that it can read secrets from Vault?
Using the AppRole which is an authentication mechanism within Vault to allow machines or apps to acquire a token to interact with Vault and using the policies you can set access limitations for your app.
It uses RoleID and SecretID for login.
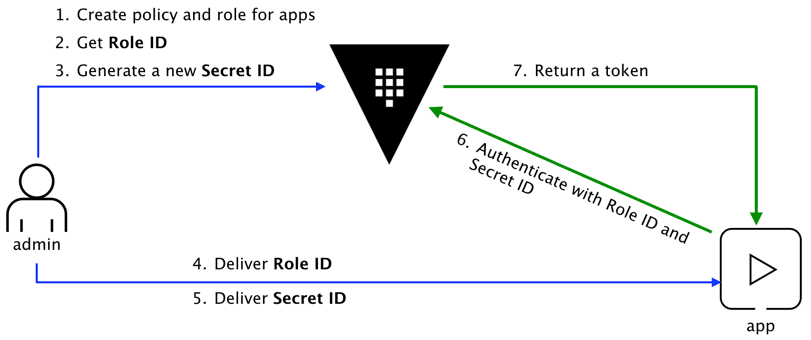
Create AppRole and policy for Jenkins
I explained how to do it in detail in my blog post: https://igorzhivilo.com/jenkins/how-to-read-vault-secrets-from-declarative-pipeline
After you applied everything I wrote in this post:
- enabled approle in vault
- v2 kv secrets engine enabled
- applied all needed policies
eventually you will getrole_idandsecret_idwhich will be used programmatically with 'python hvac'.
Another way for 3rd step (apply all needed policies) is to create policy using Vault's UI:
$ kubectl port-forward -n vault svc/vault 8200
Forwarding from 127.0.0.1:8200 -> 8200
Forwarding from [::1]:8200 -> 8200
Go to policy tab -> Create ACL Policy
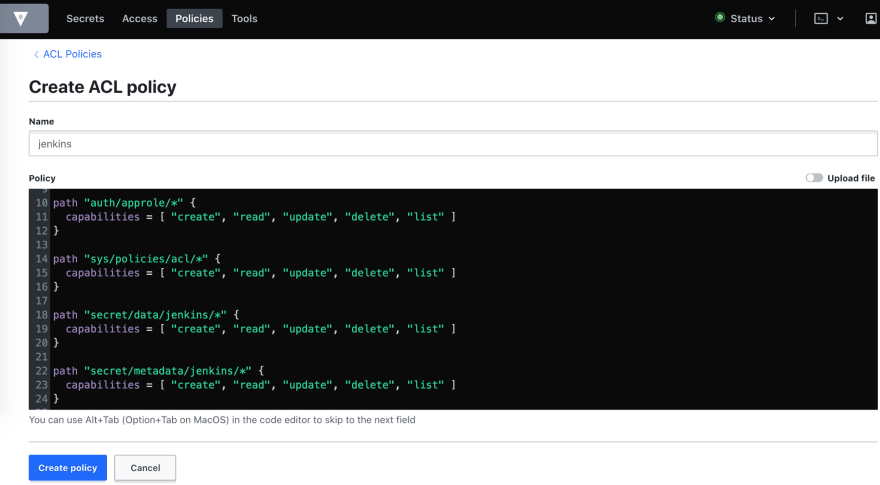
path "sys/auth/approle" {
capabilities = [ "create", "read", "update", "delete", "sudo" ]
}
path "sys/auth/approle/*" {
capabilities = [ "create", "read", "update", "delete" ]
}
path "auth/approle/*" {
capabilities = [ "create", "read", "update", "delete", "list" ]
}
path "sys/policies/acl/*" {
capabilities = [ "create", "read", "update", "delete", "list" ]
}
path "secret/data/jenkins/*" {
capabilities = [ "create", "read", "update", "delete", "list" ]
}
path "secret/metadata/jenkins/*" {
capabilities = [ "create", "read", "update", "delete", "list" ]
}
and then run via vault CLI:
$ vault write auth/approle/role/jenkins token_policies=jenkins \
token_ttl=1h token_max_ttl=4h
# Get RoleID and SecretID
$ vault read auth/approle/role/jenkins/role-id
$ vault write -f auth/approle/role/jenkins/secret-id
Test that you created correctly role_id/secret_id
$ vault write auth/approle/login \
role_id=ROLE_ID \
secret_id=SECRET_ID
Testing authentication with vault using python hvac and appRole
Simple python script to test auth with vault:
import hvac
VAULT_URL = 'http://vault.vault.svc.cluster.local:8200'
client = hvac.Client(url=VAULT_URL)
client.auth.approle.login(
role_id = self.role_id,
secret_id = self.secret_id
)
assert client.is_authenticated()
first run 'pip install hvac'.
I am running this script from pod with python container inside of my Kubernetes cluster.
URL of vault in k8s cluster: ' http://vault.vault.svc.cluster.local:8200 '
You will see authentication error if authentication is failed, if you do, make sure you applied all the needed policies, enabled applrole, and generated properly role_id / secret_id.
Validate role_id/secret_id is correct using vault CLI:
$ vault write auth/approle/login \
role_id=YOU_ROLE_ID \
secret_id=YOU_SECRET_ID
Get the list of secrets under 'jenkins' vault_prefix (CLI)
In my case,vault_prefixlooks like: 'secret/data/jenkins' and all secrets stored under 'jenkins' prefix:
$ vault kv list secret/jenkins
Keys
----
aws
git
web-app1
web-app2
...
Each key in list has additional subset of keys, for example 'aws' has access_key_id/secret_access_keys
Getting the secrets list (python)
secrets_list_response = client.secrets.kv.v2.list_secrets(path = 'jenkins')
print('The following keys are available under "jenkins" prefix: '.
format(keys=','.join(secrets_list_response['data']['keys'])))
If you have a permissions error on the secrets list, check you have access tometadata, that what you should see in UI for 'jenkins policy':
path "secret/metadata/jenkins/*" {
capabilities = [ "create", "read", "update", "delete", "list" ]
}
If you don't, add using the UI or vault CLI:
$ tee jenkins-policy-metadata.hcl <<"EOF"
path "secret/metadata/jenkins/*" {
capabilities = [ "read" ]
}
EOF
$ vault policy write jenkins jenkins-policy-metadata.hcl
Get a specific secret (python)
secret_response = client.secrets.kv.v2.read_secret(path = 'jenkins/aws')
print(secret_response)
If you have a permission error, check you have access todatain UI of Vault:
path "secret/data/jenkins/*" {
capabilities = [ "create", "read", "update", "delete", "list" ]
}
VaultHandler
I created VaultHandler which you can find here .
https://github.com/warolv/vault-backup
You can use it to:
- Dump all your secrets as encrypted yaml/json files, or you can store it without encryption.
- Get a list of your secrets.
- Print all secrets nicely.
- Populate Vault from yaml/json dumps to a specific 'vault_prefix'.
Also, I think to extend it to use different auth methods, besides appRole, create CLI, to run it in the command line and much more :-)
If the idea sounds interesting,add stars to the repo or clone it, I will know this way you like the idea.
Create Jenkins scheduled job for daily vault backup
-
I am using Vault Plugin in Jenkins https://plugins.jenkins.io/hashicorp-vault-plugin to add secrets as env variables during job execution. Read more about how to integrate this plugin into jenkins here: https://igorzhivilo.com/jenkins/how-to-read-vault-secrets-from-declarative-pipeline
-
During job execution POD will be created with 2 contaienrs: awscli to use aws s3 utility, and push created encrypted dump to private s3 bucket (vault-backups), python to run VaultHandler.*
def configuration = [vaultUrl: "$", vaultCredentialId: "vault-role-app", engineVersion: 2]
def secrets = [
[path: 'secret/jenkins/aws', engineVersion: 2, secretValues: [
[envVar: 'AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID', vaultKey: 'aws_access_key_id'],
[envVar: 'AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY', vaultKey: 'aws_secret_access_key']]],
[path: 'secret/jenkins/vault-backup', engineVersion: 2, secretValues: [
[envVar: 'VAULT_ADDR', vaultKey: 'vault_url'],
[envVar: 'ROLE_ID', vaultKey: 'role_id'],
[envVar: 'SECRET_ID', vaultKey: 'secret_id'],
[envVar: 'VAULT_PREFIX', vaultKey: 'vault_prefix'],
[envVar: 'DUMP_ENCRYPTION_PASSWORD', vaultKey: 'encryption_password']]],
]
def podTemplate = """
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
spec:
containers:
- name: awscli
image: amazon/aws-cli
command:
- cat
tty: true
- name: python
image: python:3.6
command:
- cat
tty: true
""".stripIndent().trim()
pipeline {
agent {
kubernetes {
defaultContainer 'jnlp'
yaml "$"
}
}
environment {
AWS_DEFAULT_REGION = "eu-west-1"
}
stages {
stage('Backup Jenkins'){
steps {
container('python'){
dir("$/pipelines-k8s/vault-backup/") {
withVault([configuration: configuration, vaultSecrets: secrets]){
sh """#!/bin/bash
pip install -r requirements.txt
python -u vault_handler.py
tar -zcvf vault_secrets.json.enc.tar.gz vault_secrets.json.enc
"""
}
}
}
container('awscli'){
dir("$/pipelines-k8s/vault-backup/") {
withVault([configuration: configuration, vaultSecrets: secrets]){
sh '''
aws s3 cp vault_secrets.json.enc.tar.gz s3://vault-backups/$(date +%Y%m%d%H%M)/vault_secrets.json.enc.tar.gz
'''
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
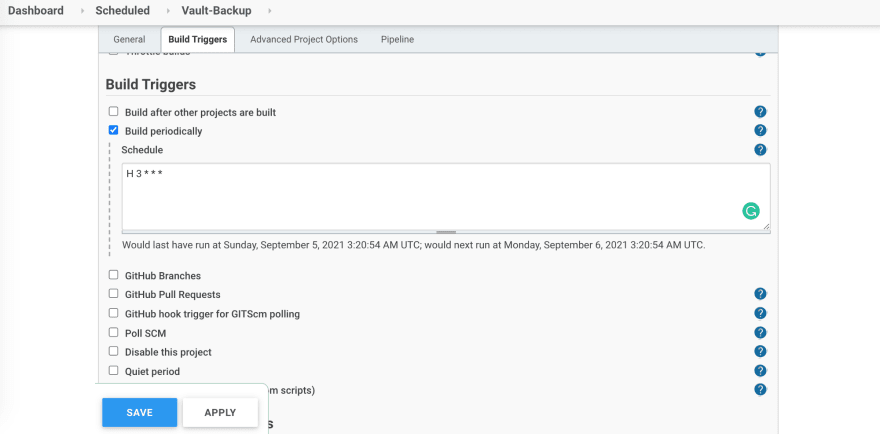
Now create a new pipeline in jenkins: newitem -> pipeline and make it periodic (daily).
In this post, I described how to automate Vault backup creation using Jenkins scheduled job and simple python script which I built to create dump of vault secrets.
Thank you for reading, I hope you enjoyed it, see you in the next post.

