
Automating GitLab Runner Setup on AWS EC2 Using Terraform

Introduction ???? As DevOps engineers, our daily tasks often involve setting up and managing...
Introduction
As DevOps engineers, our daily tasks often involve setting up and managing infrastructure to support CI/CD pipelines. Automating these processes can significantly enhance our efficiency and consistency. In this blog post, I'll walk you through provisioning and configuring aGitLab Runneron anAWS EC2instance usingTerraform. This setup will allow you to integrate GitLab CI/CD with AWS infrastructure seamlessly.
Prerequisites
Before we start, make sure you have the following:
- A GitLab account: https://gitlab.com/
- Create new group > new project on GitLab if needed, e.g:
thedevopshub/hello-gitlab.git - An active AWS account: https://signin.aws.amazon.com/signup?request_type=register
- Terraform installed on your machine
- AWS CLI installed and configured on your machine
Steps Overview
- Prepare the environment
- Configure Terraform
- Provision the GitLab Runner on AWS
- Verify GitLab CI/CD pipeline runs on new EC2 runner
- Clean up resources
NOTE:All the code for this blog post are available at: https://github.com/TheDevOpsHub/TerraformHub
Step 1: Prepare the Environment
Create an AWS Key Pair:
Follow the AWS documentation to create a key pair: https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AWSEC2/latest/UserGuide/create-key-pairs.html
Generate a GitLab Runner Registration Token:
Navigate to your GitLab project or group, then go to Settings > CI/CD > Runners, and register a new runner to get the token. Register GitLab Runner
Clone the Repository:
Clone the repository containing the Terraform configuration or create a new directory for your Terraform files.
git clone git@github.com:TheDevOpsHub/TerraformHub.git
# or creating your file manually: `mkdir TerraformHub`
cd TerraformHub
Step 2: Configure Terraform
Create a main.tf file with the following content to define the AWS resources:
resource "aws_security_group" "gitlab_runner" {
name = "gitlab-runner-sg"
description = "Security group for GitLab Runner"
ingress {
from_port = 22
to_port = 22
protocol = "tcp"
cidr_blocks = ["0.0.0.0/0"]
}
egress {
from_port = 0
to_port = 0
protocol = "-1"
cidr_blocks = ["0.0.0.0/0"]
}
}
resource "aws_instance" "gitlab_runner" {
# Check all available us-east-1 AMIs at: https://us-east-1.console.aws.amazon.com/ec2/home?region=us-east-1#AMICatalog
ami = "ami-03972092c42e8c0ca" # Amazon Linux 2 AMI
instance_type = var.instance_type
key_name = var.key_name
security_groups = [aws_security_group.gitlab_runner.name]
user_data = templatefile("install_runner.tpl", {
gitlab_runner_registration_token = var.gitlab_runner_registration_token
})
tags = {
Name = "AWS EC2 GitLab Runner"
}
}
Create an install_runner.tpl file for the user data script:
#!/bin/bash
# Install necessary dependencies
# set -x enables a mode of the shell where all executed commands are printed to the terminal
set -x
echo "Hello from EC2 user data script"
yum update -y
yum install -y curl git
# Install GitLab Runner
curl -L --output /usr/local/bin/gitlab-runner https://gitlab-runner-downloads.s3.amazonaws.com/latest/binaries/gitlab-runner-linux-amd64
chmod +x /usr/local/bin/gitlab-runner
useradd --comment 'GitLab Runner' --create-home gitlab-runner --shell /bin/bash
# Start the GitLab Runner service
/usr/local/bin/gitlab-runner install --user=gitlab-runner --working-directory=/home/gitlab-runner
/usr/local/bin/gitlab-runner start
# Register the GitLab Runner
/usr/local/bin/gitlab-runner register --non-interactive \
--url "https://gitlab.com/" \
--registration-token "${gitlab_runner_registration_token}" \
--executor "shell" \
--description "AWS GitLab Runner" \
--tag-list "aws,linux" \
--run-untagged="true" \
--locked="false"
systemctl status -l gitlab-runner.service
Create a variables.tf file to define variables:
variable "aws_region" {
description = "The AWS region to create resources in."
type = string
default = "us-east-1"
}
variable "instance_type" {
description = "The type of instance to create."
type = string
default = "t2.micro"
}
variable "key_name" {
description = "The name of the key pair to use for the instance."
type = string
default = "ec2-ssh-key" # change to yours
}
variable "gitlab_runner_registration_token" {
description = "The GitLab Runner registration token."
type = string
sensitive = true
}
Create a terraform.tfvars file:
aws_region = "us-east-1"
instance_type = "t2.micro"
key_name = "your-key-name"
gitlab_runner_registration_token = "your-registration-token"
Create an output.tf file to display outputs:
output "instance_id" {
description = "The ID of the instance."
value = aws_instance.gitlab_runner.id
}
output "instance_public_ip" {
description = "The public IP of the instance."
value = aws_instance.gitlab_runner.public_ip
}
Step 3: Provision the GitLab Runner on AWS
Initialize Terraform:
Navigate to your project directory and initialize Terraform.
terraform init
Plan the Configuration:
Create a plan to see the actions Terraform will take.
terraform plan -out "runner.tfplan"
Apply the Configuration:
Apply the Terraform plan to provision the infrastructure.
terraform apply "runner.tfplan"
Verify the Deployment:
After Terraform completes, verify that the GitLab Runner is running on the EC2 instance.
# Connect to your instance
ssh -i "your-key-name.pem" ec2-user@your-instance-public-ip
# Check GitLab Runner status
systemctl status gitlab-runner.service
On GitLab, navigate to your project > Setting > CICD > Expand the runner you would see the new active runner available.
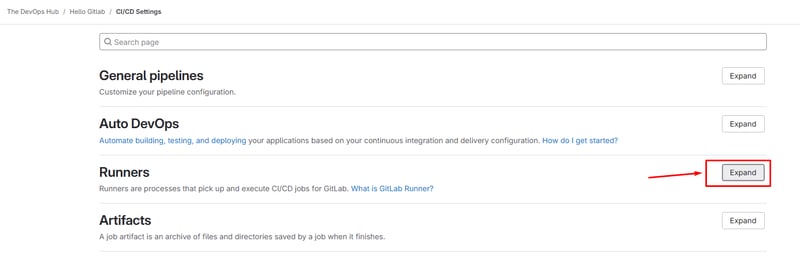
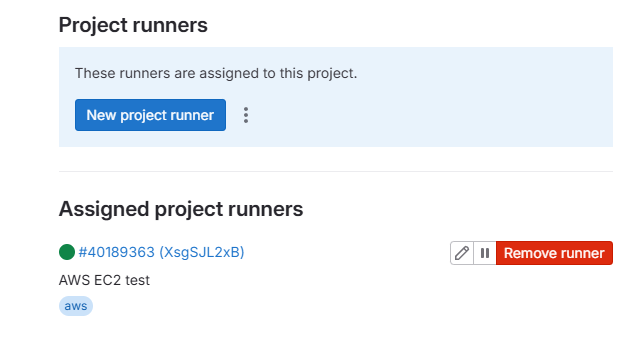
Step 4: Verify GitLab CI/CD pipeline runs on new EC2 runner
Add the .gitlab-ci.yml file to the root directory of main branch:
# .gitlab-ci.yml
stages:
- verify-runner
verify-runner:
stage: verify-runner
script:
- echo "Hello, World!"
- cat /etc/os-release
- hostname -f
- date
tags:
- aws
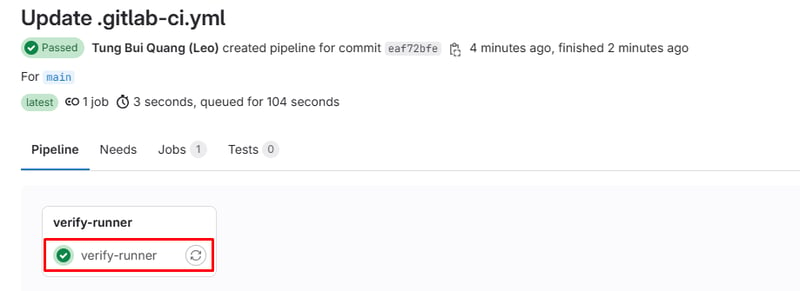
Commit the change and our pipeline will be run successfully on your newly registered EC2 runner:
Pipeline flow:
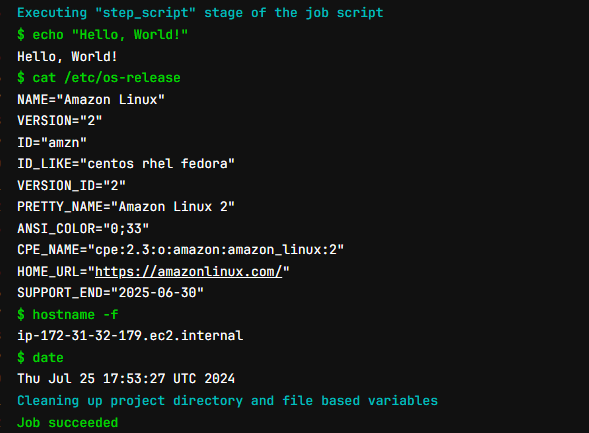
Logs:
Step 5: Clean Up Resources
Once you no longer need the runner, you can destroy the resources to avoid unnecessary costs:
terraform destroy
Conclusion
By following these steps, you can automate the setup of a GitLab Runner on AWS EC2 using Terraform. This approach not only saves time but also ensures consistency and repeatability in your CI/CD pipeline infrastructure. If you have any questions or suggestions, feel free to leave a comment below.

