A Workflow for Deploying Application Code with Terraform

Introduction As infrastructure as code (IaC) continues to transform the way applications...
Introduction
As infrastructure as code (IaC) continues to transform the way applications are managed and deployed, tools likeTerraformandTerraform Cloudprovide powerful solutions for managing cloud infrastructure and deploying application code efficiently. Let's walk through a step-by-step workflow for deploying application code using Terraform and integrating version control systems (VCS) while securing sensitive variables.
Prerequisites
Before diving into the workflow, ensure the following:
- Terraform is installed locally.
- A Terraform Cloud account is set up.
- A version control system (e.g., GitHub) is configured with your Terraform project.
- Necessary cloud provider credentials are available (e.g., AWS).
Step 1: Set Up a Terraform Cloud Workspace
- Log intoTerraform Cloudand create a new workspace.
- Link the workspace to your version control system (e.g., GitHub repository).
- Select the desired branch to track (commonly
mainordevelop).
Terraform Cloud will now monitor this branch for changes and trigger runs accordingly.
Step 2: Write Terraform Configuration Files
-
Define your infrastructure in
.tffiles within the GitHub repository:- Example for deploying an AWS EC2 instance:
provider "aws" { region = "us-west-2" } resource "aws_instance" "example" { ami = var.ami_id instance_type = "t3.micro" tags = { Name = "TerraformExampleInstance" } } -
Include a
variables.tffile to define input variables, such as AMI IDs or database credentials. -
Add a
terraform.tfvarsor.auto.tfvarsfile to supply default variable values, excluding sensitive ones.
Step 3: Secure Sensitive Variables
Sensitive variables, such as API keys and passwords, should never be hardcoded in your configuration files. Instead, secure them in Terraform Cloud:
- Navigate to theVariablestab of your workspace.
- Add sensitive variables (e.g.,
db_password) underEnvironment VariablesorTerraform Variables. - Ensure
AWS_ACCESS_KEY_IDandAWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEYare stored as environment variables for authentication.
Step 4: Push Changes to GitHub
-
Commit your Terraform configuration to the GitHub repository:
git add . git commit -m "Add initial Terraform configuration" git push origin main -
Terraform Cloud automatically detects changes in the repository and initiates aPlanrun to evaluate the proposed changes.
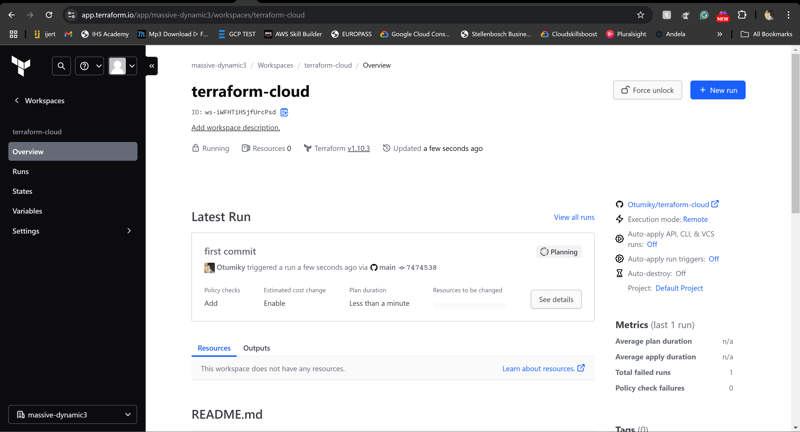
Step 5: Review and Approve Plan
- Navigate to theRunstab in Terraform Cloud.
- Review the plan to ensure the changes match your expectations.
- Approve the plan to apply the changes (if manual approval is enabled).
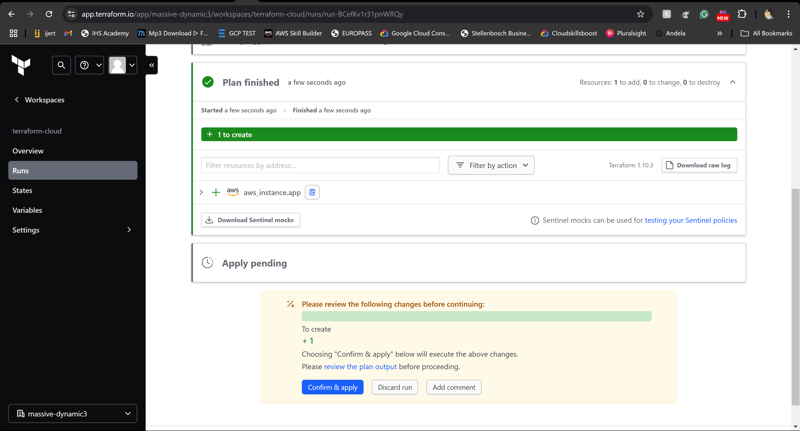
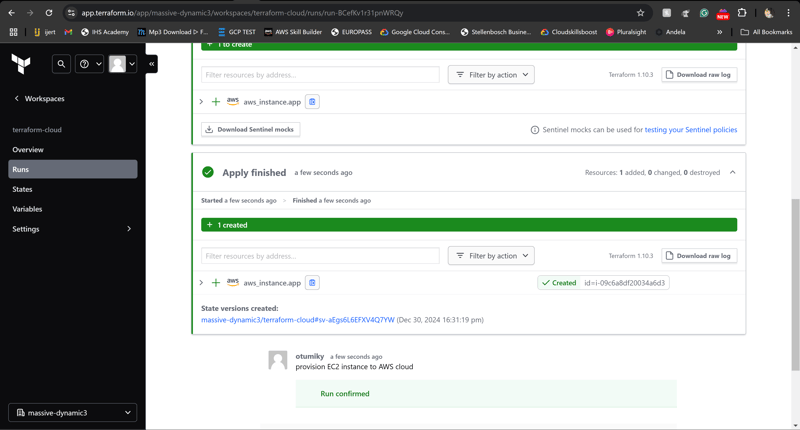
Step 6: Deploy the Application
Once the plan is approved, Terraform Cloud automatically applies the changes, provisioning the necessary infrastructure and deploying the application code.
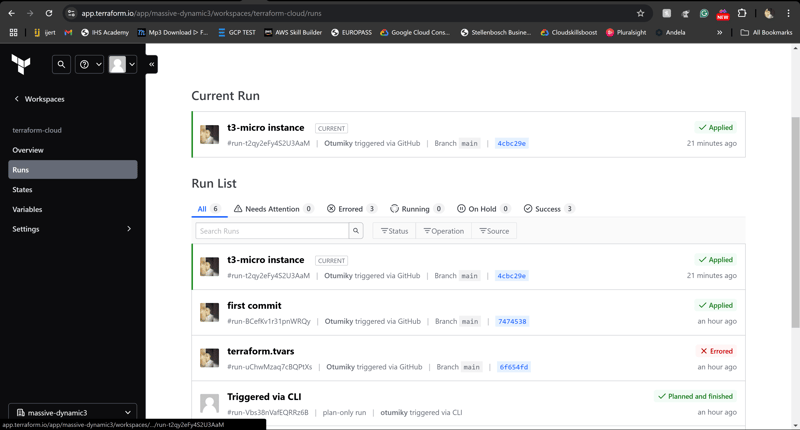
Step 7: Manage Updates
- To make updates, modify the Terraform configuration files locally.
- Push the changes to the tracked branch in the GitHub repository.
- Terraform Cloud triggers a new Plan and Apply cycle, reflecting the updates in your infrastructure.
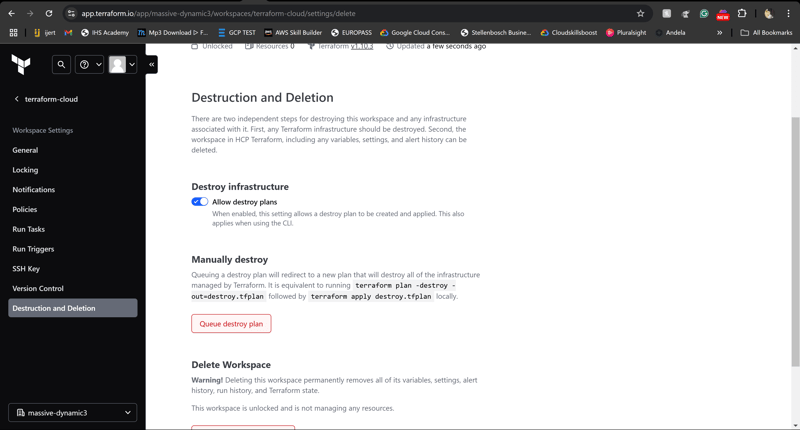
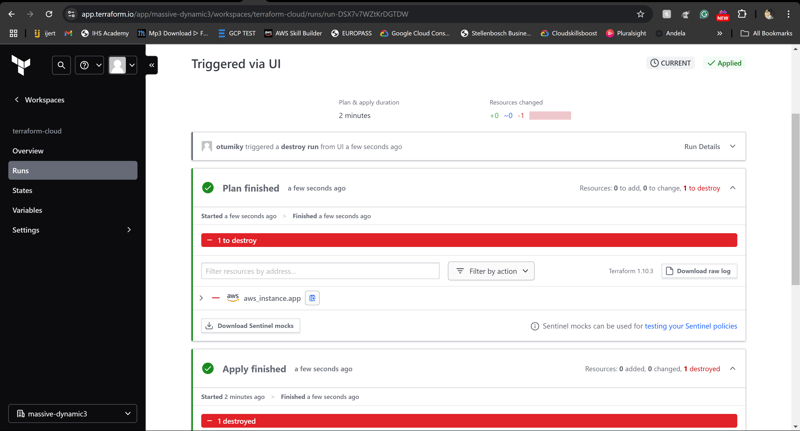
Don't forget to destroy the infrastructure after completing the task. Headover to settings>Destruction and deletion, then hit "Queue destroy plan"
Advantages of This Workflow
- Version Control Integration: GitHub acts as the single source of truth, ensuring a streamlined and auditable process.
- Automation: Terraform Cloud automates infrastructure deployment, reducing manual intervention and errors.
- Security: Sensitive variables are securely managed, avoiding exposure in code repositories.
- Scalability: The workflow supports a range of cloud providers and resource types, adapting to diverse infrastructure needs.

